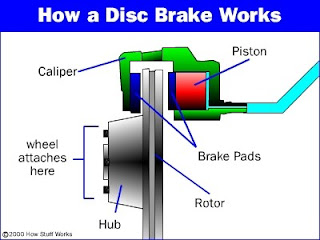
Trickling down from the motocross world, disc brakes have now become popular on off-road bicycles. Discs provide powerful and reliable braking in all types of weather and terrain so they’re ideal for trail riding. Plus, unlike rim brakes, discs aren’t compromised should you hit a hole or land hard and bend your wheel.
Working Principle of Ultrasonic Machining
The time spent on ultrasonic machine entirely depends on the frequency of the vibrating tool. It also depends on the size of grains of the abrasive slurry, the rigidity and the viscosity as well. The grains used in the abrasive fluid are usually boron carbide or silicon carbide as they are rigid than others. The used abrasive can be carried away easily if the viscosity of the slurry fluid is less.
Ultrasonic Machining Advantages and Disadvantages
Get to know about the advantages and disadvantages of machining process in order to make the right decision:
Advantages
- Machined all sorts of hard materials
- Produces fine finished and structured results
- Produces less heat
- Various hole cut shapes due to vibratory motion of the tool
Disadvantages
- Requires a higher degree of integrity and skills
- No certified record of radiography
- Unnecessary large grain sizes causes defects
- Additional repairs might be required due to spurious signs and misunderstanding of the process
Ultrasonic machines are the future of machining which is used all over the world for creating hard and brittle forms of materials for the industrial uses. A lot of operations can be performed with the ultrasonic machine which can benefit the industrialists in a variety of ways. The advanced technology creates solution which helps in opening up the market opportunities and has made things easier.