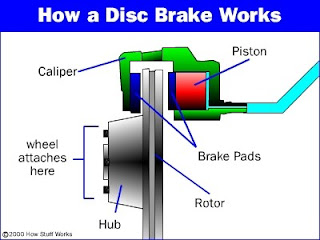
Trickling down from the motocross world, disc brakes have now become popular on off-road bicycles. Discs provide powerful and reliable braking in all types of weather and terrain so they’re ideal for trail riding. Plus, unlike rim brakes, discs aren’t compromised should you hit a hole or land hard and bend your wheel.
Sunday, 4 September 2016
DIFFERENCE BETWEEN OPEN DIE FORGING AND CLOSED DIE FORGING
Forging Processes: Open Die Forging & Closed Die Forging
There are multiple options for metal deformation using the forging concept. The two most common processes are open and closed die forging. While similar in the basic idea of using pressure and temperature to modify material, the two types of forging are made distinct by their use of dies to form the metal.
Open Die Forging
Open die forging is the process of deforming a piece of metal between multiple dies that do not completely enclose the material. The metal is altered as the dies “hammer” or “stamp” the material through a series of movements until the desired shape is achieved. Products formed through open forging often need secondary machining and refining to achieve the tolerances required for the finished specifications. Open die forging is often used for short run forgings of parts that are simple, rather than complex, in design, such as discs, rings, sleeves, cylinders and shafts. Custom shapes can also be produced with open die forging. The repeated working of the material through the deformation process increases the strength of the grain structure. Some additional benefits of open die forging include improved fatigue resistance and strength. Open die forging also reduces voids.
Closed Die Forging
Closed die forging (also referred to as impression die forging) is a metal deformation process that uses pressure to compress a piece of metal to fill an enclosed die impression. In some closed die forging processes, a succession of impression dies are used to modify the shape of the material into the final desired shape and form. The type of material, tightness of tolerances, and need for heat treatment can determine the number of passes the product requires through the dies.
There are two types of equipment that are commonly used for closed die forging: mechanical forging presses and hydraulic forging presses.
WHAT IS AN OIL FILTER AND HOW OIL FILTERS ARE MADE
An oil filter is a filter designed to remove contaminants from engine oil, transmission oil, lubricating oil, or hydraulic oil. Oil filters are used in many different types of hydraulic machinery, but primarily in internal-combustion engines, in on- and off-road motor vehicles, light aircraft, and various naval vessels.
 You’ve may have put many new filters on your car when changing the oil, but have you ever seen inside one or how and what are they made of?
You’ve may have put many new filters on your car when changing the oil, but have you ever seen inside one or how and what are they made of?
 You’ve may have put many new filters on your car when changing the oil, but have you ever seen inside one or how and what are they made of?
You’ve may have put many new filters on your car when changing the oil, but have you ever seen inside one or how and what are they made of?
About 400 million oil filters are manufactured in the USA each year. Take a look at the process of making oil filters!
Main components of a gear box:
In any device two or more component works together and fulfills the required function. In a transmission box four components are required to fulfill its function. These components are-
1. Counter shaft:
Counter shaft is a shaft which connects with the clutch shaft directly. It contains the gear which connects it to the clutch shaft as well as the main shaft. It may be run runs at the engine speed or at lower than engine speed according to gear ratio.
2. Main shaft:
It is the shaft which runs at the vehicle speed. It carries power form the counter shaft by use of gears and according to the gear ratio, it runs at different speed and torque compares to counter shaft. One end of this shaft is connects with the universal shaft.
3. Gears:
Gears are used to transmit the power form one shaft to another. They are most useful component of transmission box because the variation is torque of counter shaft and main shaft is depend on the gear ratio. The gear ratio is the ratio of the driven gear teeth to the driving gear teeth. If gear ratio is large than one, the main shaft revolves at lower speed than the counter shaft and the torque of the main shaft is higher than the counter shaft. On other hand if the gear ratio is less than one, than the main shaft revolves at higher speed than the counter shaft and the torque of the main shaft is lower than the counter shaft. A small car gear box contains four speed gear ratio and one reverse gear ratio.
4. Bearings:
Whenever the rotary motion, bearings are required to support the revolving part and reduce the friction. In the gear box both counter and main shaft are supported by the bearing.
Working of a principle gear box:
In a gear box, the counter shaft is mashed to the clutch with a use of a couple of gear. So the counter shaft is always in running condition. When the counter shaft is bring in contact with the main shaft by use of meshing gears, the main shaft start to rotate according to the gear ratio. When want to change the gear ratio, simply press the clutch pedal which disconnect the counter shaft with engine and change connect the main shaft with counter shaft by another gear ratio by use of gearshift lever. In an gear box, the gear teeth and other moving metal must not touch. They must be continuously separated by a thin film of lubricant. This prevents excessive wear and early failure. Therefor a gearbox runs partially filled with lubricant oil.
AIR CONDITIONING SYSTEM OF AN AUTOMOBILE
We all know about air conditioning system. The automotive air conditioning system is also works on the reverse Brayton or Rankine cycle. As like all air conditioning system the aim of automotive air conditioning is to control the temperature and humidity of the atmospheric air and circulate the same in the automobile. The automotive air conditioning system consists a refrigeration system, air circulation and distribution system and a control system. The refrigeration system cool down the air which include many other parts like compressor, condenser etc. The air circulating system circulate this cooled air into the car which include blower, air duct etc. The controlling system used to control the temperature of the car by sensing it and control the refrigerating system.
Principle of Car Air Conditioning System:
The automotive air conditioning system includes the compressor, condenser, evaporator, receiver-dehydrator and connecting lines which includes expansion valve, orifice tube, suction throttling valve, positive operating absolute valve, evaporator pressure regulator valve, thermal sensor, high pressure cut off switch and cycling compressor switch. In old days Freon 12 was used as refrigerant but now it is replaced by alternative refrigerant like R134a. The layout of refrigerating system is as shown in figure.
Working of Car Air Conditioning System:
The working of automotive air condition system is similar to all other air conditioning system. The refrigerant vapour from the evaporator is compressed to high pressure by the compressor. The compressor is driven by the engine through a belt drive. It is connected by a electromagnetic clutch witch serve engage and disengage the compressor required. A variable displacement AC compressor is sometime used to match compressor capacity to varying cooling requirement. Refrigerant pressure and temperature increases in the compressor and convert it into vapour form. This high pressure and temperature refrigerant vapour from the compressor then discharge to the condense, which is a heat exchanger situated in front of vehicle. In the condenser the refrigerant liberate heat and convert into liquid form. Sometime the ram air is not sufficient so an extra engine or electric driven fan is used to cool down the refrigerant. This cooled but high pressure refrigerant allow to pass form dehydrator to extract any moisture. Dry refrigerant liquid is then made to pass through expansion valve mounted at the inlet side of the evaporator. The expansion valve allows the refrigerant liquid to expand to low pressure in the evaporator. The process of expansion to low pressure makes the refrigerant to evaporate and thereby cool the evaporator. A sensing devices, called temperature tube signals the diaphragm in the expansionvalve to vary orifice size depending upon the refrigerant temperature at the evaporator outlet, thus achieving automatic temperature control. The evaporator is similar in construction to the condenser.
The same circulation and distribution system as used for ventilation and heating system. The air from the blower is forced to flow over the evaporator coils which remove the latent heat of vaporization, moisture and impurities form the air. Condenser moisture with the impurities fro the evaporator drips into a try form where the same are drained out. This system is microprocessor based and depending upon input signals outside air temperature, inside air temperature, mode selection and desired temperature setting, automatically controls the air mixer valve, re-circulation valve etc.
Precaution while using car AC system:
- Do not use AC fresh air mode open always, since this mode is for occasional use just to release the air in circulation for a long time.
- Never operate AC with heater on.
- Never run AC without refrigerant otherwise compressor may seize.
- Do not leave AC joints open which may cause the moisture to enter the system.
- Do not charge the refrigerant in the AC system before flushing.
- Never switch on the AC at high speeds, which may result in the seizing of compressor.
Tips for maintenance of car AC system:
- Clean the condenser during normal servicing.
- Maintain correct refrigerant level. Less refrigerant would result in less cooling, while excessive would also result lesser cooling and excessive tripping.
- Top up the compressor with adequate oil.
- Clean the evaporator periodically.
- Maintain proper belt tension. A loose belt will slip whereas overtight belt would cause noise and premature compressor failure.
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)